Threat Context Monthly May 2025: Scattered Spider & Lumma Stealer
Welcome to the Threat Context Monthly blog series where we provide a comprehensive roundup of the most relevant cybersecurity news and threat information from KrakenLabs, Outpost24’s cyber threat intelligence team. Here’s what you need to know from May about Scattered Spider, Lumma Stealer and more.
Threat actor of the month: Scattered Spider
Three major UK retailers—Marks & Spencer, Co-op and Harrods—have all reported ransomware incidents that began with seemingly routine help-desk interactions. In the M&S case, attackers convinced support staff to reset an employee’s password, then allegedly deployed the DragonForce encryptor that locked down internal systems. In the following days, similar password-reset schemes and network infiltrations hit Co-op and Harrods, forcing each company to shut down affected services and prompting the National Cyber Security Centre to remind organizations to treat any unexpected support requests with extreme caution.
A great deal of speculation has focused on a loose online community nicknamed “Scattered Spider”. Rather than a single gang, this label describes English-speaking cybercriminals—often in their early twenties—who share social-engineering know-how on platforms like Discord and Telegram. Between mid-2022 and mid-2024, individuals linked to these methods are thought to have worked as affiliates for ransomware services such as BlackCat, RansomHub and Qilin, using impersonation, SIM swapping and MFA-bypass tricks to win initial access. Although several suspects were arrested in 2024, the community’s full makeup remains unclear, and there could be copycat threat actors continuing to leverage the same playbook.
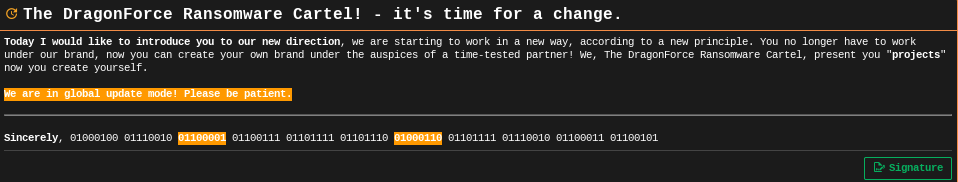
Adding another layer of uncertainty, multiple sources report that the encryptor used against M&S—and allegedly in the Co-op and Harrods attacks—belonged to the DragonForce Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operation. DragonForce’s own operators are said to have contacted the BBC, providing screenshots and data samples as proof of their network breaches and large-scale data theft. While there’s no definitive evidence that Scattered Spider worked directly with DragonForce this time, the overlap of social-engineering techniques and the known history of these hackers partnering with RaaS providers makes the theory a strong—but still unconfirmed—possibility.
Scattered Spider TTPs
Their core method exploits the human element: impersonating employees or contractors to persuade service-desk agents to reset passwords, disable MFA or provision privileged accounts. By mimicking internal processes, using spoofed numbers and demonstrating fluent, localized English, they slip past defenses in minutes without triggering alerts.
Spotlight threat: International operation against Lumma Stealer
“Lumma Stealer” is an information stealer written in a combination of C++ and ASM and sold in underground forums and in Telegram since December 2022 under a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) scheme.
Lumma steals browser credentials and cookies, and autofill data from Chromium, Mozilla, and Gecko-based browsers, steals cryptocurrency wallets, collects VPN data, email clients, FTP clients, and Telegram applications. Furthermore, it harvests user documents and system data.
The information stealer was developed and commercialized by the underground user “Shamel” a Russian-located threat actor. Since its inception Lumma stealer has become very popular within the cybercriminal community and the developer mentioned in an interview that it had more than 400 active clients in late November 2023. The malware’s popularity continued growing, and Lumma detections grew exponentially during the H2 of 2024 becoming one of the most prolific infostealers.
In late May 2025, the Microsoft Digital Crimes Unit, together with the US Department of Justice, EUROPOL, Japan’s Cybercrime Control Center and various cybersecurity vendors, performed a coordinated disruption operation against Lumma infostealer. Following a US court order, Microsoft seized and facilitated the takedown, suspension, and blocking of approximately 2,300 Lumma infrastructure malicious domains.

Threat actors using Lumma Stealer
Since its inception Lumma stealer has been used by multiple threat actors. Prolific ransomware groups such as “Black Basta” “Scattered Spider”, “Interlock”, “Storm-1607”, “Storm-1113/Payk_34”, or “TA577/ Storm-1674” have included it in their toolset.
Furthermore, within the traffers ecosystem relevant adversaries such as “FatherOfCarders”, “LogsDiller”, “Moon Cloud” or “TA2727”, among many others, also utilize Lumma to perform their malicious activities.
KrakenLabs observed highlights
Ransomware
LockBit leaks: A LockBit ransomware administration panel was hacked, resulting in the leak of sensitive data, including private messages between affiliates and victims, Bitcoin wallet addresses, affiliate accounts, and information about malware and infrastructure. LockBit downplayed the incident, claiming no victim data or decryptors were compromised. Learn more / and more →
Coinbase suffered extortion: Cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase disclosed a data breach performed by insiders, who were bribed by threat actors. The breach affected 69,000 customers, and the malicious actors demanded a ransom of US$ 20 million. The company declined to pay and instead offered a reward of US$ 20 million in exchange for information about the authors. Learn more →
Supply chain
E-commerce stores backdoored: A supply chain attack affecting 500–1,000 e-stores, including a US$40 billion multinational, through 21 backdoored Magento extensions from vendors Tigren, Meetanshi, and Magesolution (MGS). These backdoors, hidden for six years, were only recently abused, allowing remote control via a manipulated license check file. Learn more →
Geopolitics
Hacktivist activity related to India-Pakistan conflict: In the wake of recent kinetic escalations between India and Pakistan, at least 45 hacktivist groups have become active, with 10 aligned as pro-India and 35 as pro-Pakistan. This situation highlights how geopolitical conflicts now consistently drive cyber activity. Defacement and DDoS attacks are the most common tactics observed. Learn more →
Vulnerabilities
New European Vulnerability Database (EUVD): The European Union’s cybersecurity authority ENISA has announced the new European Vulnerability Database (EUVD) is operational. The information comes from multiple sources such as open-source databases, CSIRTs, or vendors advisories. EUVD offers three different dashboard views: critical vulnerabilities, exploited vulnerabilities, and EU coordinated ones. Learn more → / and more →
Law enforcement
Operation Endgame announced new targets: International law enforcement coalition “Operation Endgame” launched an operation against the ransomware kill chain by targeting initial access malware strains: Bumblebee, Latrodectus, Qakbot, Hijackloader, DanaBot, Trickbot and Warmcookie. The operation coordinated by Europol took down 300 servers worldwide, disrupted 650 domains, seized EUR 3.5 million in cryptocurrency and issued international arrest warrants against 20 targets. Learn more→
Spyware vendor fined: A US federal jury has ordered Israeli spyware vendor NSO Group to pay US$167 million in punitive damages and US$444,719 in compensatory damages to WhatsApp for a 2019 campaign that targeted 1,400 users with Pegasus spyware. This case marks the first time a spyware vendor has been held accountable in court, setting a precedent for the industry. Learn more →
Legislation
New Japan’s cyberdefense law: Japan enforced the new Active Cyberdefense Law which allows offensive cyber operations. The new bill explicitly allows law enforcement agencies to infiltrate and neutralize hostile servers before any malicious activity has taken place and provides government with the power to analyze foreign internet traffic entering or transiting through Japan networks. Learn more →
What’s new in Threat Context this month?
Threat actors: Albabat, NightSpire, MonsterV2, Blucoder, Mora_001, Crypto24, Cyb3rDrag0nz, RA Lord, Dragon ransomware, Devman, IMN Crew, QatarRat, dark software, Moon Cloud, BEARHOST, KatzStealer, kiemdev05 and more!
Tools: Gremlin Stealer, Albabat, PipeMagic, MonsterV2, PlayBoy Locker, IOCONTROL, Amatera Stealer, QWCrypt, QatarRat, PE32 Ransomware, Noodlophile, Katz Stealer, Pronsis Loader, and more!
Add threat intelligence to your organization
Outpost24’s External Attack Surface Management (EASM) platform gives users access to Digital Protection modules powered by our human-led threat intelligence team, KrakenLabs. Get in touch to learn more.