Threat Context Monthly: Executive intelligence briefing for February 2024
Welcome to the Threat Context Monthly blog series where we provide a comprehensive roundup of the most relevant cybersecurity news, and threat information from KrakenLabs, Outpost24’s cyber threat intelligence team.
Threat actor of the month: Cactus Ransomware group
“Cactus Group” is a ransomware group that has been active since at least March 2023. At first, the group only engaged in single extortion through a messaging service known as TOX (meaning that they only required a ransom in return for the decryption key, and there was no blackmail regarding a potential data leak). However, since July 2023, they started using their own Data Leak Site (DLS), threatening their victims by publishing the stolen data. Thus, Cactus Group is following the double-extortion technique, but it remains unknown if they operate under the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) business model.
After analyzing the victims they already shared within their DLS, Outpost24 KrakenLabs analysts can confirm that, at the time of writing, the US is the preferred country for the group, followed by the UK and Canada. Cactus Group has been targeting several industries, with construction, automotive and manufacturing being the most affected.
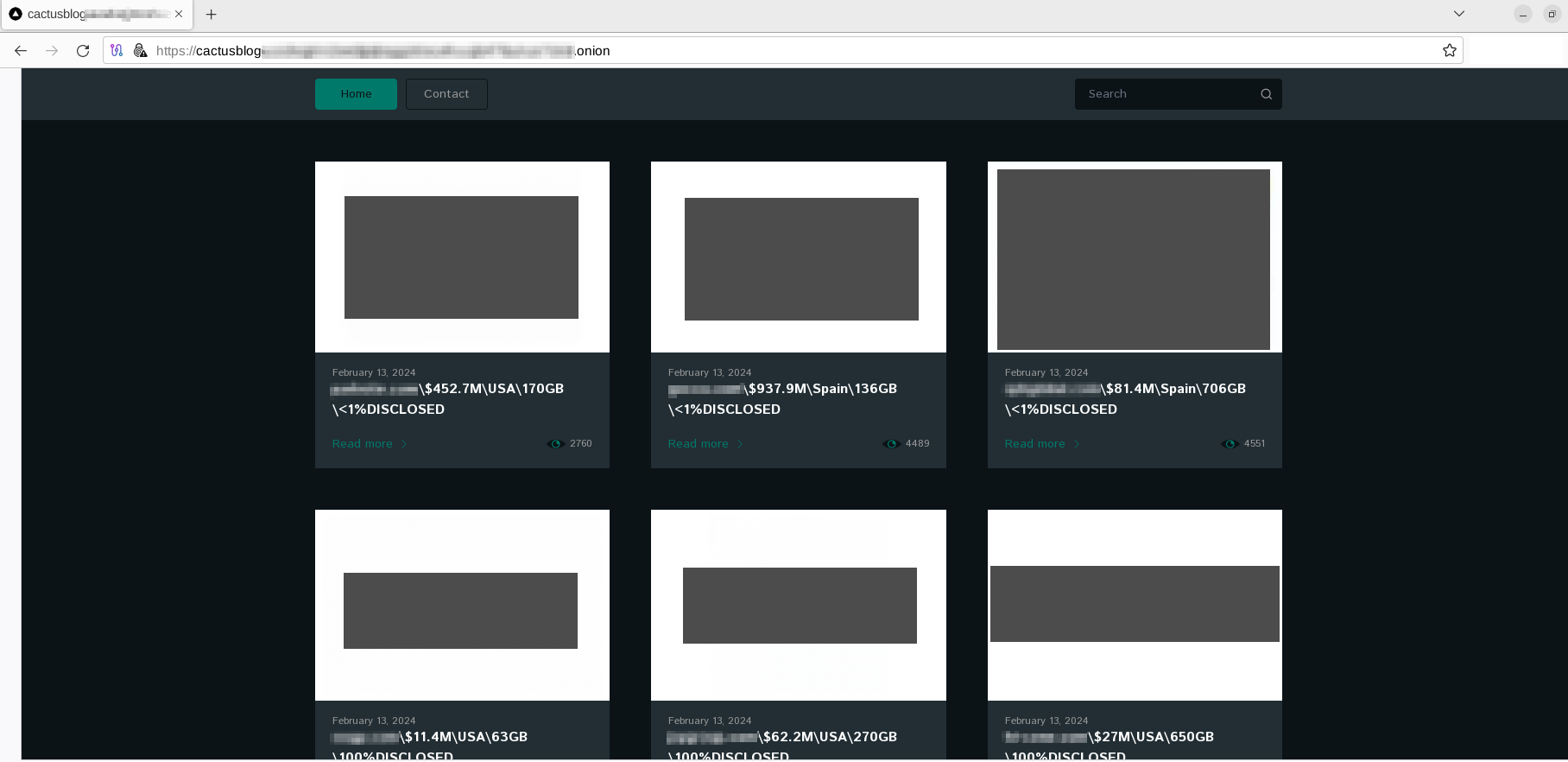
Initial Access Vector (IAV): Exploitation of public-facing vulnerabilities related to VPN services.
Toolkit: A ransomware strain targeting Windows dubbed Cactus ransomware.
Relationships with other threat actors:
- Threat actor “UNC2198”, known for deploying Maze and Egregor, was observed in November 2023 deploying Cactus ransomware by using Danabot malware, which was previously distributed through advertising campaigns.
- Researchers from Sophos and Kroll have highlighted similar behavior patterns between Cactus Group’s incidents and several ransomware operations, including “Black Basta”, “Hive Gang“, and “Royal Group“.
These relations with other groups’ incidents led Outpost24 KrakenLabs analysts to suggest that Cactus Group could indeed operate a RaaS program.
Spotlight threat: Vulnerable Ivanti VPNs
CISA has issued an emergency directive to federal agencies regarding two actively exploited zero-day flaws affecting Ivanti Connect Secure and Ivanti Policy Secure products; an authentication bypass (CVE-2023-46805) and a code injection bug (CVE-2024-21887). When exploited together, these vulnerabilities allow malicious actors to execute arbitrary commands on vulnerable systems.
Ivanti disclosed the flaws on January 10 and initially shared some mitigation guidelines until a patch was finally released. Moreover, the group addressed additional vulnerabilities affecting these same products (CVE-2024-21888 and CVE-2024-21893) that had also been exploited in the wild.
Further details about the exploitation came from Volexity and Mandiant researchers, who in December 2023, detected the previously undocumented “UTA0178”, a likely Chinese nation-state group exploiting them. In mid-January, Rapid7 released a Proof of Concept (PoC) showing the implementation of this exploit chain and other threat actors besides UTA0178 started to exploit the vulnerability.
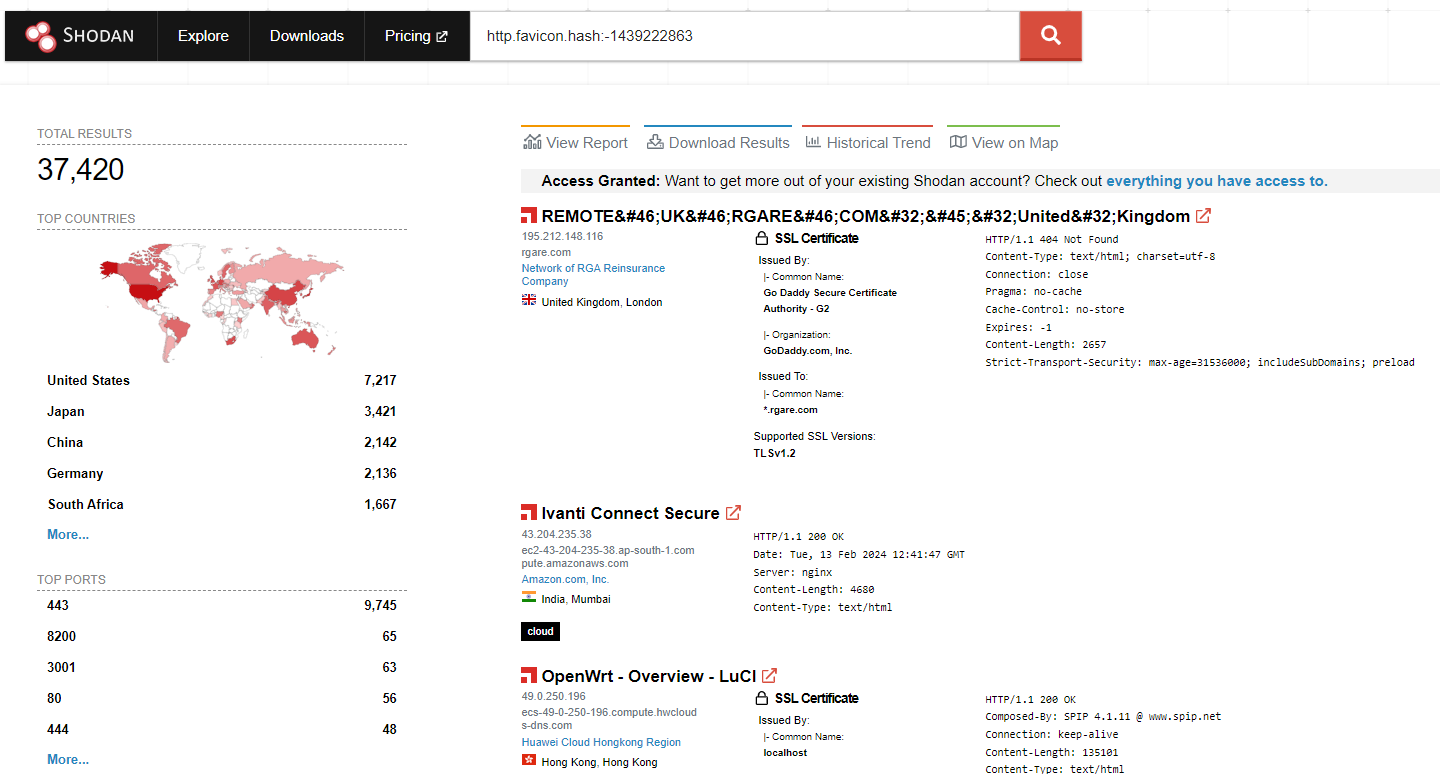
Outpost24 KrakenLabs’ analysts found 37,420 Ivanti exposed servers via Shodan. Censys has reported 412 servers have been compromised with a backdoor.
KrakenLabs highlights
Emerging threats
Artificial Intelligence: A finance worker at a multinational firm located in Hong Kong was tricked into paying out $25 million to fraudsters using deepfake technology to pose as the company’s chief financial officer in a multi-person video conference call. Learn more →
Botnets: NetScout reported that malicious botnet activity is reaching unprecedented levels. The spikes originated from five key countries: the US, China, Vietnam, Taiwan, and Russia. Learn more →
Vulnerabilities
Commercial spyware vendors were behind more than half of the total 0-day vulnerabilities Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) discovered in 2023. Learn more →
Ransomware
Payments: Chainalysis reported that ransomware gangs have reached a historical unprecedented milestone during 2023, surpassing $1 billion in extorted cryptocurrency payments from victims. Learn more →
Extortion methods: Ransomware victims were targeted by fake hack-back offers from a threat actor posing as a security researcher, offering to delete stolen data for a fee, in multiple incidents involving either Royal or Akira ransomware groups. Learn more →
Learn more about Threat Compass
Want more? Get started with Threat Compass to receive the latest actionable intelligence from our world-class in-house analyst team.
What’s new in Threat Context this month?
Threat actors: Storm-1152, Smishing Triad, SelfZer0, TheDyer, UTA0178, Meow Leaks, isabellavonbiz, Cactus Gang, qwqdanchun, Vextrio, TA571, Blackwood, etc.
Tools: FalseFont, Kasseika, Spica, Blank Grabber, HeadLace, Phemedrone, HULK, SpectralBlur, VIRTUALPITA, VIRTUALPIE, VajraSpy, Krustyloader, NSPX30, Zipline, Thinspool, etc.
and much more!
